
Breeding program management
The IRRI irrigated breeding program
.gif)
To describe the pedigree method at IRRI
Describe naming of pedigree at IRRI
Describe crosses at IRRI
Describe types of crosses
Demonstrate IRRI nurseries
What is the pedigree method?
The pedigree method owes its name to the pedigree record of selected plants maintained to trace ancestral relationship among such plants
A detailed description of present day pedigree method was outlined by Love (1927)
In this method individual plants are selected starting with F2 and in the subsequent segregating generations their progenies are tested till the progenies become homozygous.
During the entire operation a record of all parent-offspring relationship is kept: PEDIGREE RECORD
In this method each progeny in every generation can be traced back to the original F2 plant The pedigree describes the parents, the grandparents, great-grandparents, and so on.
How is the naming of pedigree at IRRI?
The naming at IRRI is based on the cross number and the serial numbers of selected plants
-->IR numbers are assigned consecutively to the crosses (now IR80389) made at IRRI just before the hybrid seeds are incubated for germination
-->When plant selections are made from F2 and subsequent generations of an IR cross, numerical designations are given for each breeding line
Let's take an example:
IR2061-214-3-8-2 (IR28)
1. Selections from the F2 were grown in the pedigree nursery as F3 rows: IR2061-1, ------IR2061-214 -----and so on up to IR2061-806
2. From selection 214, three plants were grown as F4 selections:IR2061-214-1, IR2061-214-2 and IR2061-214-3
3. From selection IR2061-214-3, 10 plants were again selected as F5 rows. These selections were designated as IR2061-214-3-1 up to 2061-214-3-10
4. From selection IR2061-214-3-8, three plant selections were made and planted in the pedigree nursery as F6 rows IR2061-214-3-8-1, IR2061-214-3-8-2 and IR2061-214-3-8-3
5. At maturity selection IR2061-214-3-8-2 appeared uniform and was bulk harvested and evaluated in replicated trials.
What is the procedure at IRRI?
First we look at the breeding objectives
High Yield Potential?
Short Growth Duration?
Superior Grain Quality?
Multiple disease and insect resistance?
Then we choose the parents.
There are donors for various traits (Hybridization Block)
IRRI Varieties are currently used as donors in various programs as
like irrigated, rainfed, flood prone and hybrid rice programs.
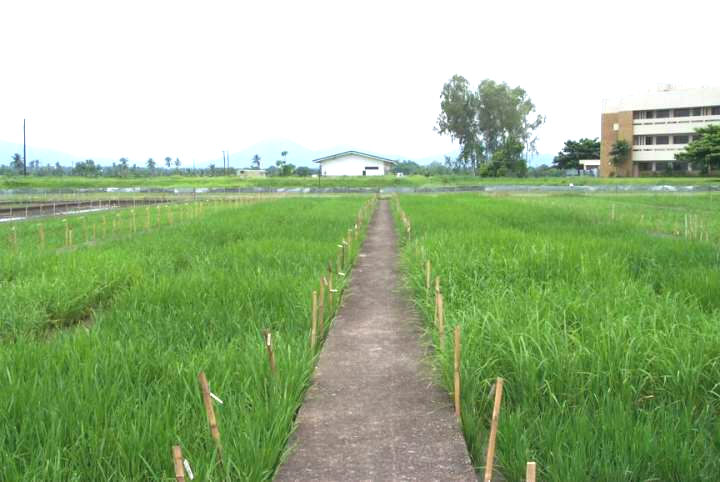

The hybridization block at IRRI
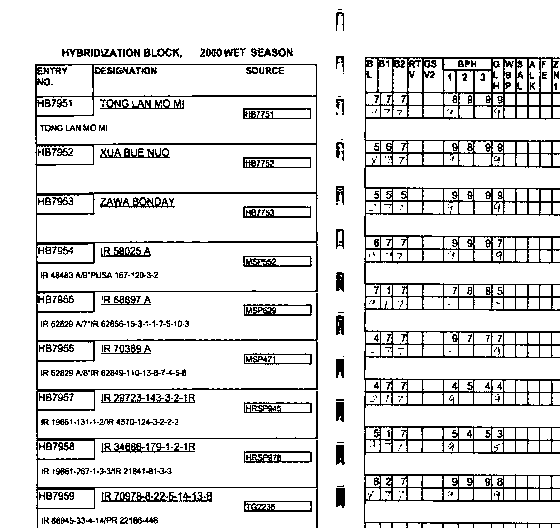
Records of the hybridization block are kept in a "Field book"
Examples of crosses...
To further improve indica germplasm for yield, grain quality and incorporation of resistance to diseases and insects:
Released varieties x Elite Indica Lines
Elite Indica Lines x Elite Indica Lines
Elite Indica Lines x Basmati Type Lines
To develope Basmati type germplasm:
Basmati x Elite Indica Lines
Basmati x Basmati Type Derivatives
Basmati Type Derivatives x Basmati Type Derivatives
To improving tropical Japonicas for temperate regions (e.g. Korea)
Tropical Japonica x Tropical Japonica crosses
Tropical Japonica x Korean Varieties
To further improve NPT's (New Plant Type) for yield, grain quality and incorporation of resistance to diseases and insects:
Improved NPTs x Improved NPTs
Improved NPTs x Released Indica Varieties
Improved NPTs x Elite Indica Varieties
At IRRI we have the following types of crosses:
Single crosses
Backcrosses
Three way/Top crosses
Around 900 crosses are made yearly (during the wet & the dry season)
The F1 nursery
--> 2-6 rows (30 Plants) per cross are grown.
--> the off-types are rouged and accidental selfs are identified
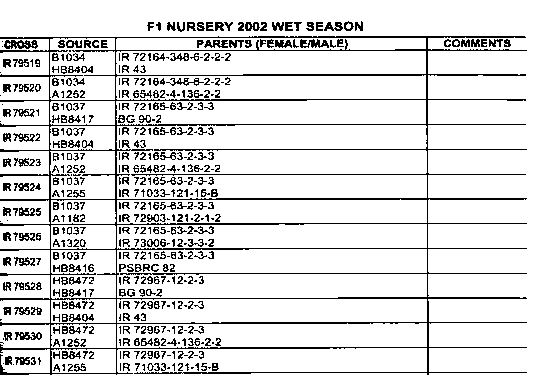
Example of a F1 nursery field book
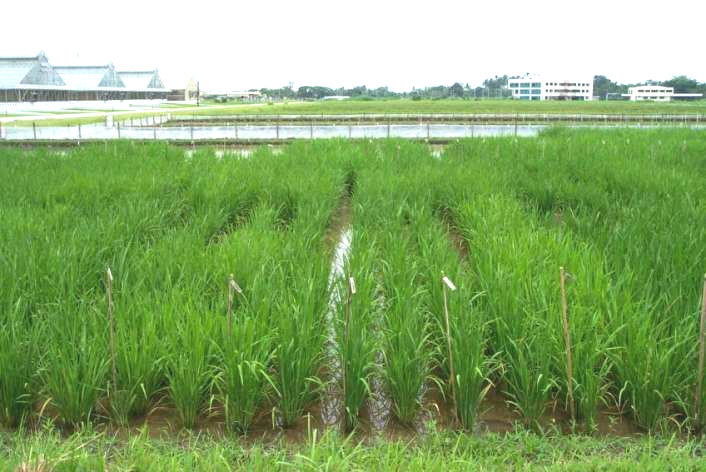

The IRRI F1 nursery
The F2 nursery
There is a "protected" part and an "unprotected" part. The lines in the protected are in general susceptible to diseases and insects. In the unprotected part they are in general resistant to diseases and insects.


IRRI's protected (left) and unprotected (right) F2 nursery
First lines are grown in a blast nursery where they are inoculated with BB Race1/Race2. (For more on blast and BB, please go to the lesson: "Breeding for disease resistance")
The susceptible or undesirable plants are rejected.
The desirable plants are harvested (usually 100 to 500 plants)
The space between plants is 35 x 25 cm, the population size ranges from 2,500 to 5,000 individuals

Design of the blast nursery
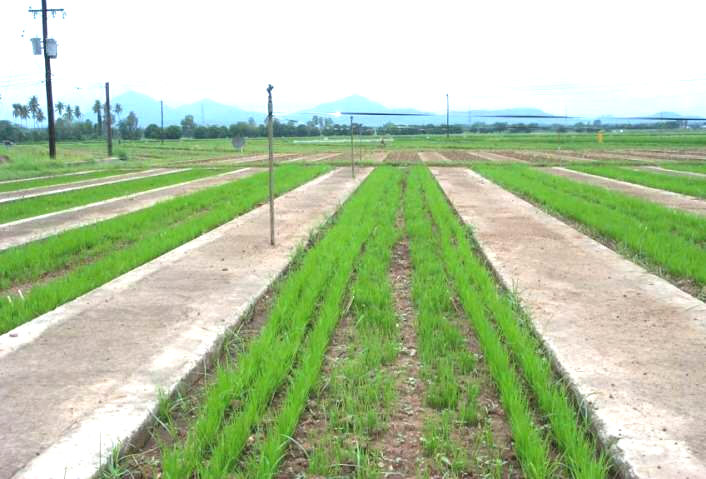

IRRI's blast nursery
The pedigree nursery
There are 4 nurseries per year at IRRI:
January & July (Unprotected)
May & November (Protected)
The space between plants is 30 x 20 cm. 16,000 to 20,000 rows of30 plants are planted. In every 20th row is a check variety (4 Checks) planted.
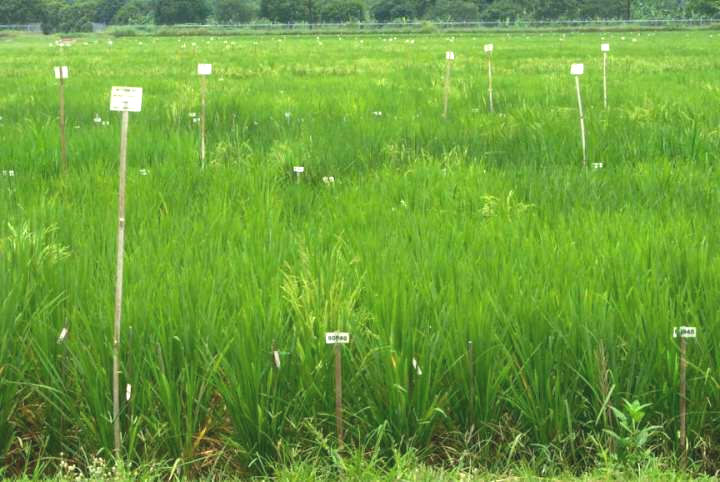

The IRRI pedigree nursery in May

The IRRI pedigree nursery in July
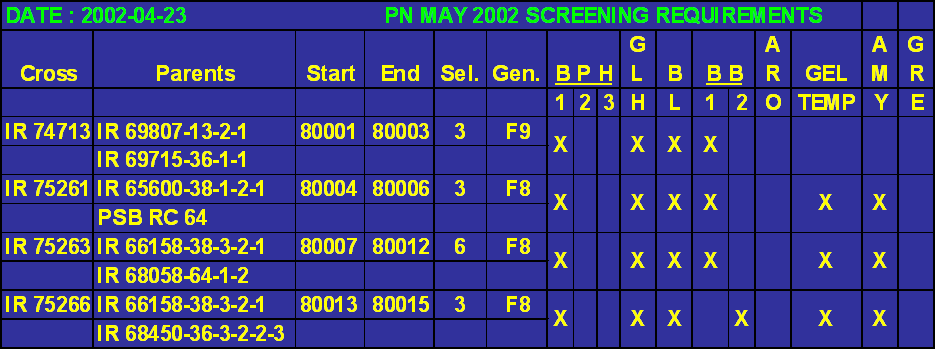
The electronic fieldbook of the IRRI pedigree nursery in May
The F3 is in single rows. From the F4 onwards there are 3/6 rows.
The selection between rows/within rows must be at least 3 plants.
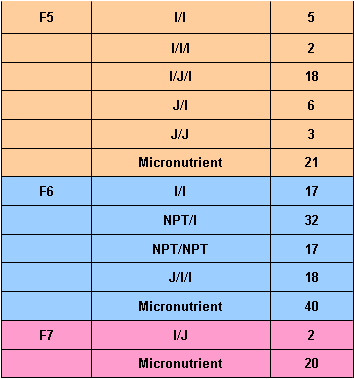
17811 Progeny rows
The composition of the IRRI pedigree nursery of November 2004 was as follows:
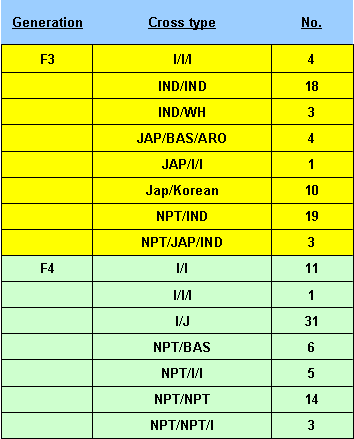
Exercises/Questions
What are the merits and demerits of the pedigree method?
Do you practice pedigree method of breeding, if yes, how does it differ from the one followed at IRRI?
In your pedigree program selections are done for how many traits?
In your opinion, under what circumstances pedigree method of breeding should not be followed?
What other alternative breeding method/s would you recommend?
![]()
Click here to open a powerpoint on IRRI's pedigree program
![]()
Next lesson
In the next lesson we will learn more about the traits that determine the quality of grain.
