Storage
 The purpose of any grain storage facility is to provide safe storage conditions for the grain in order to prevent grain loss caused by adverse weather, moisture, rodents, birds, insects and micro-organisms like fungi.
The purpose of any grain storage facility is to provide safe storage conditions for the grain in order to prevent grain loss caused by adverse weather, moisture, rodents, birds, insects and micro-organisms like fungi.
In general, it is recommended that rice for food purposes be stored in paddy form rather than milled rice as the husk provides some protection against insects and helps prevent quality deterioration.
However, when rice can be stored as brown rice, 20% less storage capacity will be needed. Brown rice is rice grain with its hulls removed but not polished. Under tropical conditions brown rice has a very short shelf life, approximately two weeks.
Storage systems
Rice storage facilities take many forms depending on the quantity of grain to be stored, the purpose of storage, and the location of the store.
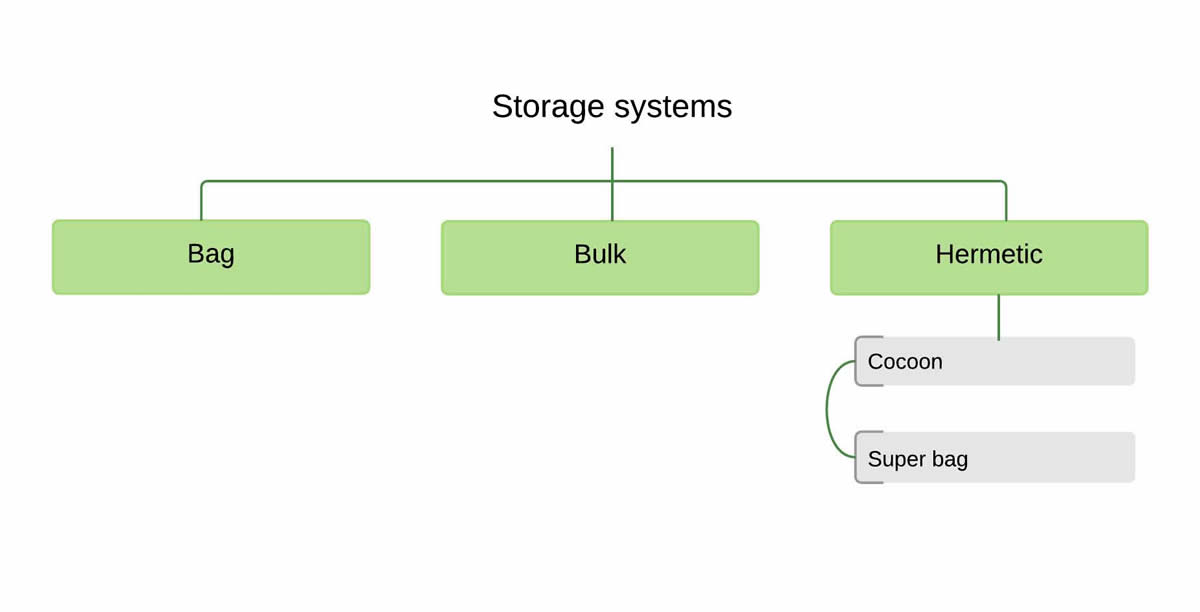
Storage systems can be through bag, bulk, or hermetic containers.
- Bag storage- grain is stored in 40−80 kg bags made from either jute or woven plastic
- Bulk storage - grain is stored in bulk at the farm or at commercial collection houses
- Hermetic storage - grain is stored in an airtight container so that that moisture content of the stored grain will remain the same as when it was sealed. These storages can extend germination life of seeds, control insect grain pests, and improve headrice recovery. Examples include:
- IRRI Superbag - available to farmers and processors at low cost
- Cocoon - commercially available
- Other locally available containers - useful in rural settings, where local containers can be easily converted into hermetic storage systems
Guidelines for safe storage
 Good storage systems include (1) protection from insects, rodents and birds, (2) ease of loading and unloading, (3) efficient use of space, (4) ease of maintenance and management, and (5) prevention of moisture re-entering the grain after drying.
Good storage systems include (1) protection from insects, rodents and birds, (2) ease of loading and unloading, (3) efficient use of space, (4) ease of maintenance and management, and (5) prevention of moisture re-entering the grain after drying.
Safe storage of rice for longer periods is possible if three conditions are met:
- Grain is maintained at moisture levels of 14% or less and seed is stored at 12% or less
- Grain is protected from insects, rodents and birds
- Grain is protected from re-wetting by rain or imbibing moisture from the surrounding air
The longer the grain needs to be stored, the lower the required moisture content will need to be. Grain and seed stored at moisture contents above 14% may experience the growth of molds, rapid loss of viability and a reduction in eating quality.
Good hygiene in the grain store or storage depot is important in maintaining grain and seed quality. To maintain good hygiene in storage:
- Keep storage areas clean. This means sweeping the floor, removing cobwebs and dust, and collecting and removing any grain spills.
- Clean storage rooms after they are emptied and this may include spraying walls, crevices and wooden pallets with an insecticide before using them again.
- Placing rat-traps and barriers in drying and storage areas. Cats deter and help control rats and mice.
- Inspect storage room regularly to keep it vermin proof.
- Inspect the stored seeds once a week for signs of insect infestation. When necessary and only under the direction of a trained pest control technician, the storage room or the seed stock may be sealed with tarpaulin and treated with fumigants.
Specific challenges in the humid tropics
Rice grain is hygroscopic and in open storage systems the grain moisture content will eventually equilibrate with the surrounding air at the so called equilibrium moisture content (EMC). High relative humidity and high temperatures typical for the humid tropical climate lead to grains absorbing water in storage and to a high final moisture content.
In many tropical countries, the equilibrium moisture content is above safe storage moisture levels.