Re-circulating batch dryer
What is a re-circulating batch dryer?
A dryer is a mechanical device or machine that removes the water from wet grains by forcing either ambient air or heated air through the grain bulk. In a re-circulating dryer, the same quantity of grain is re-cycled through the dryer until the final moisture content is reached.
What are the advantages of a re-circulating batch dryer?
Re-circulating batch dryers have a number of advantages over the cheaper fixed-bed batch dryers:
- Very small floor space is required.
- Continuous mixing of the grains results in very low moisture content variation.
- During circulation, the grain is tempered, which improves drying efficiency and grain quality.
- Automatic controls with automatic shutoff make the dryer virtually fully automatic.
The principle behind the re-circulating batch dryer?
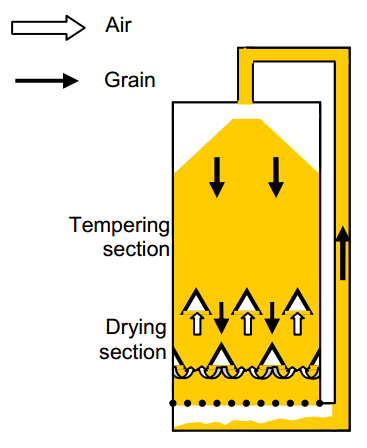
As illustrated below, the grain is constantly moving through the drying bin from top to bottom, passing first the tempering section and then the drying section. Retention time for one pass is around 60 min. Drying rate is around 1−2% per hour. Drying air temperature is up to 55°C.
For more information:
Visit the Rice Knowledge Bank website (http://www.knowledgebank.irri.org), email postharvest@irri.org; or call +63 2 580 5600.
Types of re-circulating batch dryers
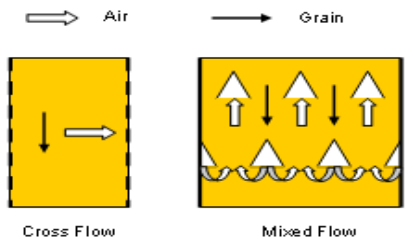
Depending on airflow relative to grain flow, there are two different types of re-circulating dryers (Fig. 1):
- Cross flow: simpler construction, better with wet grain.
- Mixed flow: Better grain quality from better mixing
Components of a re-circulating batch dryers
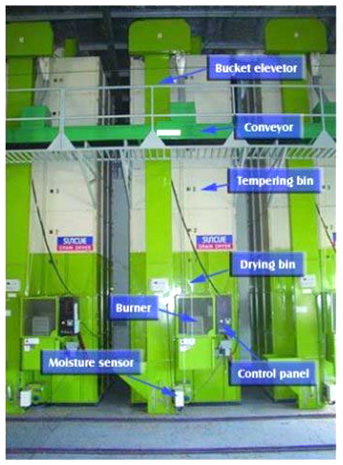
A re-circulating batch dryer consists of:
- Drying and tempering bin for holding the grains
- Bucket elevators and conveyors for circulating, loading, and unloading grains
- Burner for heating the drying air
- Electronic controller and on-line moisture meter for controlling the drying operation