Vietnamese flat-bed dryers SGH4 and SGH8
 What is a flat-bed dryer?
What is a flat-bed dryer?
A dryer is a machine that removes the water from wet grains by forcing heated air through the grain bulk. In a flat-bed dryer, the same quantity of grain is kept stationary in a holding bin until drying is completed.
What is the capacity of a flat-bed dryer?
In Southern Vietnam, 3 t/batch is the minimum capacity for economies of scale. On the other hand, 10 t/batch is the maximum size in terms of labor management. Size is selected on the basis of harvest season duration. On average, drying time is 7 h depending on the initial moisture content. Thus, an x t/batch dryer can dry 2.5x t/d, or 100x t per drying season of about 40 days. For example, the 8 t/batch dryer can dry 20 t/d or 800 t per drying season.
Why do we use a flat-bed dryer?
The flat-bed dryer has these features:
- Easy to operate
- Can be used for rice and corn
- Gives better quality grain compared with sun drying
- Simple design allows local production and ensures easy maintenance and repair
- Can be operated with an engine if electricity is not available or is very expensive
How do we operate a flat bed dryer?
- Check oil and fuel levels of the engine, the pulley tension and make sure the dryer is operational. Consult your manual.
- Load the drying bin evenly. If the grain contains lots with different moisture content, mix these well before drying.
- Start the motor or engine.
- For very wet grain, aerating the grains for 30-60 min before drying will improve quality but increase drying time and fuel consumption.
- Start the heater.
- Monitor moisture content and temperature every hour. Stop drying when the moisture content in the middle of the bulk (half grain depth) reaches the desired final moisture content.
Considerations
Thu-Duc District, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam
- For seeds drying air temperature should not exceed 43°C
- Increasing the temperature reduces drying time but results in uneven drying.
- Increasing the airflow shortens drying time and reduces moisture content but increases energy cost.
- Mixing during drying reduces the moisture gradient.
Technical specifications
| Drying performance | |
| Capacity | 4 (SHG4) - 8 (SHG8) t/batch |
| Grain depth | 0.25m |
| Drying air temperature | 43 - 45 oC |
| Drying rate | 1.5 % h-1 |
| Drying bin | |
| Usually made of bricks or concrete | |
| Grain floor | |
|
|
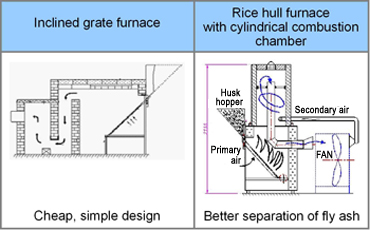
| Fan and heater options | |
| Fan | Axial vane type |
| Air delivery 1 | 1 + 0.1 m3 s-1 t-1 |
| Pressure creation | 300 Pa |
| Rice hull consumption | 6.25 kg h-1 t-1 capacity |
| (One ton of paddy contains approx. 200 kg of rice hull) | |
| Drive options | |
| Diesel engine | 3 hp |
| Fuel consumption | 0.2-0.4 l diesel h-1 t-1 capacity |
| Electric motor | 2 hp |
With information from:
Center for Agricultural Energy and Machinery Nong Lam University, NLU Thu-Duc District, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam. Email: phhien@hcm.vnn.vn.
For more information:
email postharvest@irri.org; or call +63 2 580 5600