How to manage water
 Rice is typically grown in bunded fields that are continuously flooded up to 7−10 days before harvest.
Rice is typically grown in bunded fields that are continuously flooded up to 7−10 days before harvest.
Continuous flooding helps ensure sufficient water and control weeds.
Lowland rice requires a lot of water.
On average, it takes 1,432 liters of water to produce 1 kg of rice in an irrigated lowland production system. Total seasonal water input to rice fields varies from as little as 400 mm in heavy clay soils with shallow groundwater tables to more than 2000 mm in coarse-textured (sandy or loamy) soils with deep groundwater tables.
Worldwide, water for agriculture is becoming increasingly scarce. Due to its semi-aquatic ancestry, rice is extremely sensitive to water shortages.
To effectively and efficiently use water and maximize rice yields, the following good water management practices can be done:
Different crop establishment methods require different water management practices:
For continuous flooding
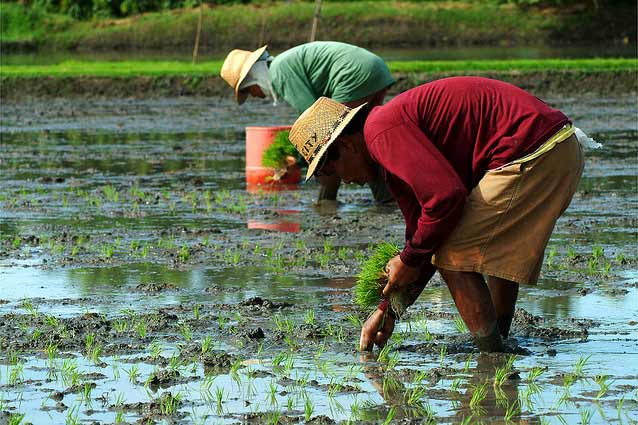 Continuous flooding of water generally provides the best growth environment for rice.
Continuous flooding of water generally provides the best growth environment for rice.
After transplanting, water levels should be around 3 cm initially, and gradually increase to 5−10 cm (with increasing plant height) and remain there until the field is drained 7−10 days before harvest.
For direct wet seeded rice, field should be flooded only once the plants are large enough to withstand shallow flooding (3-4 leaf stage).
Lowland rice is extremely sensitive to water shortage (below saturation) at the flowering stage. Drought at flowering results in yield loss from increased spikelet sterility, thus fewer grains.
Keep the water level in the fields at 5 cm at all times from heading to the end of flowering.
In case of water scarcity, apply water-saving technologies such as Alternate Wetting and Drying (AWD) and consider changing planting method from puddled transplanting to non-puddled transplanting or dry-direct seeding.
FAQ: What's the difference between dry seeded rice (DSR) and aerobic rice?
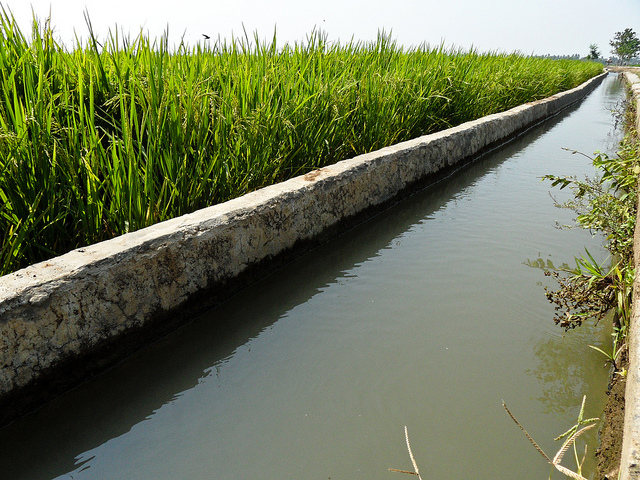
 The construction of separate channels to move water to and from each field greatly improves the control of water by individual farmers.
The construction of separate channels to move water to and from each field greatly improves the control of water by individual farmers.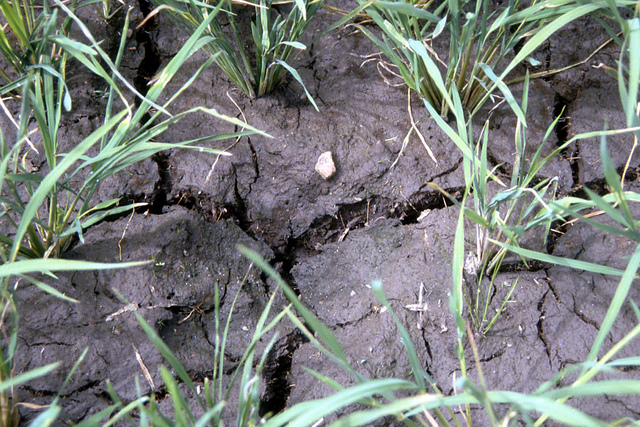 Perform shallow tillage operations before land soaking. This fills in the cracks and can greatly reduce the amount of water used in land preparation.
Perform shallow tillage operations before land soaking. This fills in the cracks and can greatly reduce the amount of water used in land preparation.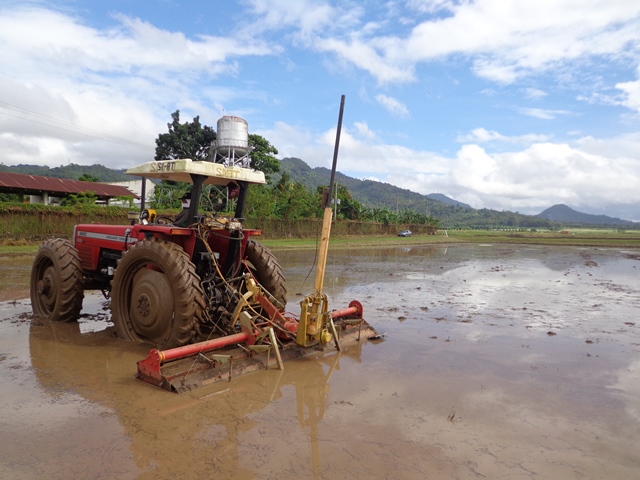  A well-leveled field is crucial to good water management. An unleveled field requires an extra 80−100 mm of water to give complete water coverage. This is nearly an extra 10% of the total water requirement to grow the crop.
A well-leveled field is crucial to good water management. An unleveled field requires an extra 80−100 mm of water to give complete water coverage. This is nearly an extra 10% of the total water requirement to grow the crop. 
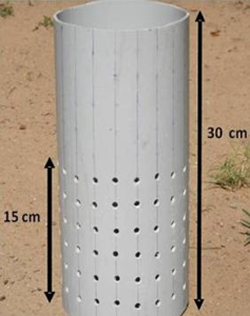 can be started a few weeks (1-2) after transplanting. Irrigate and then allow the water depth to drop to 15 cm below the surface using a field water tube (pictured to the right) to monitor the water level depth. Once the water level has dropped to 15 cm below the surface, re-flood the field to a depth of 5 cm above the surface and repeat. From one week before to one week after flowering, the field should remain flooded. After flowering, during grain filling and ripening, the water level can drop to 15 cm below the surface before re-flooding.
can be started a few weeks (1-2) after transplanting. Irrigate and then allow the water depth to drop to 15 cm below the surface using a field water tube (pictured to the right) to monitor the water level depth. Once the water level has dropped to 15 cm below the surface, re-flood the field to a depth of 5 cm above the surface and repeat. From one week before to one week after flowering, the field should remain flooded. After flowering, during grain filling and ripening, the water level can drop to 15 cm below the surface before re-flooding. 








